- In relativistic dynamics, the kinetic energy is defined as the
difference between the total energy and the rest energy
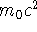 . Suppose that an electron has a momentum of
. Suppose that an electron has a momentum of
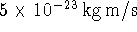 . Calculate the
electron's kinetic energy using
. Calculate the
electron's kinetic energy using
- relativity theory, and
- classical mechanics.
- Suppose that the above electron's position is measured to an
accuracy of
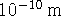 , a distance
equivalent to the radius of a
small atom. What is the minimum
uncertainty in the momentum after the measurement? Is
the disturbance in the momentum significant?
[3 marks]
, a distance
equivalent to the radius of a
small atom. What is the minimum
uncertainty in the momentum after the measurement? Is
the disturbance in the momentum significant?
[3 marks] - Calculate the de Broglie wavelength of the above electron. Could a beam of electrons of this kinetic energy be used to visualize the positions of atoms in a material sample? Explain briefly. [3 marks]
- Write down the ground-state electronic configuration of a germanium atom. [4 marks]
- Would a germanium atom be paramagnetic or diamagnetic? [2 marks]
- During the calibration of a constant-volume
calorimeter, a 1.0095g
sample of benzoic acid (
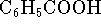 )
is burned completely in an excess of oxygen. The temperature
rises by
)
is burned completely in an excess of oxygen. The temperature
rises by 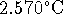 . The heat capacities of
reactants and products are negligible compared to the heat
capacity of the calorimeter. What is the heat capacity
of the calorimeter? The specific change in internal energy on
combustion of benzoic acid is
. The heat capacities of
reactants and products are negligible compared to the heat
capacity of the calorimeter. What is the heat capacity
of the calorimeter? The specific change in internal energy on
combustion of benzoic acid is 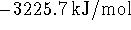 .
[5 marks]
.
[5 marks] - A 1.1243g sample of solid sucrose
(
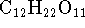 ) is then burned in the same
calorimeter. The temperature rises by
) is then burned in the same
calorimeter. The temperature rises by 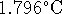 .
What is the specific energy of combustion of sucrose?
[5 marks]
.
What is the specific energy of combustion of sucrose?
[5 marks]
- Accurately calculate
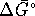 for the reaction
for the reaction

at 210K. The standard enthalpy of formation of ozone at
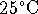 is 142.7kJ/mol.
The standard molar entropies of ozone and of oxygen
at the same temperature
are, respectively, 238.82 and
is 142.7kJ/mol.
The standard molar entropies of ozone and of oxygen
at the same temperature
are, respectively, 238.82 and
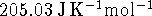 while the constant-pressure heat
capacities are, respectively, 39.2 and
while the constant-pressure heat
capacities are, respectively, 39.2 and
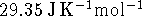 . [10 marks]
. [10 marks] - Calculate
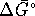 for the above reaction
at 210K
under the assumption that neither
for the above reaction
at 210K
under the assumption that neither 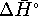 nor
nor 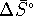 vary significantly with
temperature. Is the result significantly different?
[3 marks]
vary significantly with
temperature. Is the result significantly different?
[3 marks] - Calculate the equilibrium pressure of ozone under the conditions prevailing at an altitude of 20km. [7 marks]
- Bonus:
- The above calculation gives a value for the
partial pressure of ozone at 20km
which is much, much too low. Why?
![]()
where A is a constant and ![]() Derive this equation and compute a value for the constant
A. Explain the physical significance of the number 4
appearing in the above equation. [8 marks]
Derive this equation and compute a value for the constant
A. Explain the physical significance of the number 4
appearing in the above equation. [8 marks]
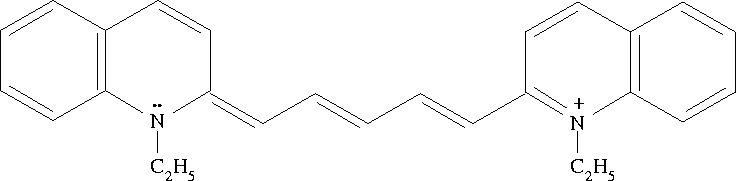
Figure 1: The 1,1'-diethyl-2,2'-dicarbocyanine ion. Cyanine dyes
such as this one absorb strongly in the visible range
and thus are brightly colored compounds. Accordingly, they
have traditionally been used as dyes. This particular
dye absorbs strongly at the red end of the spectrum,
giving it a pleasant blue-green color.
This transition is due to the molecular orbital which follows
the chain of conjugated ![]() bonds (alternating single and
double bonds) between the two nitrogen
atoms. This orbital can be treated as a one-dimensional
box. In the ground state, electrons occupy
all of the energy levels up to n=5 (the highest occupied
molecular orbital, HOMO). Absorption is due to a HOMO to LUMO
(lowest unoccupied molecular orbital) transition. Given this
information, what is the length of the ``box''? The average
length of carbon-carbon bonds in
conjugated
bonds (alternating single and
double bonds) between the two nitrogen
atoms. This orbital can be treated as a one-dimensional
box. In the ground state, electrons occupy
all of the energy levels up to n=5 (the highest occupied
molecular orbital, HOMO). Absorption is due to a HOMO to LUMO
(lowest unoccupied molecular orbital) transition. Given this
information, what is the length of the ``box''? The average
length of carbon-carbon bonds in
conjugated
![]() chains is 0.14nm. Is this data consistent with the
results of your calculation and with the description of the
orbital given above?
[10 marks]
chains is 0.14nm. Is this data consistent with the
results of your calculation and with the description of the
orbital given above?
[10 marks]