![]()
Unfortunately, the equilibrium constant for the reaction is very small. What could you do to get a reasonable yield of the product? [5 marks]
- Calculate the maximum work which can be performed
per mole of glucose
at 298K from the oxidation of aqueous glucose by sulfur.
The products are aqueous carbon disulfide and water
and the concentrations of glucose and of
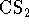 are, respectively, 0.2 and
are, respectively, 0.2 and 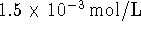 . The standard free energy of
formation of aqueous carbon disulfide is approximately
75kJ/mol. [5 marks]
. The standard free energy of
formation of aqueous carbon disulfide is approximately
75kJ/mol. [5 marks]
- Compare your answer to question 5a to the maximum work which
can be obtained from the oxidation of aqueous glucose by
aqueous oxygen under similar conditions, i.e. 0.2mol/L
glucose,
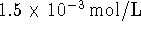
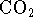 and
and 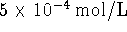 dissolved oxygen. Is there an advantage to using one or
the other oxidizing agent? [5 marks]
dissolved oxygen. Is there an advantage to using one or
the other oxidizing agent? [5 marks]
![]()
Suppose that you want to carry out this reaction at 298K
in a rigid reactor with initial pressures of
![]() and HF of 1 and 15atm, respectively. What
are the equilibrium pressures of all reactants and products?
[10 marks]
and HF of 1 and 15atm, respectively. What
are the equilibrium pressures of all reactants and products?
[10 marks]
Hint: A little thought about the size of the equilibrium constant leads to an approximate method of solution which gives a reasonable answer.