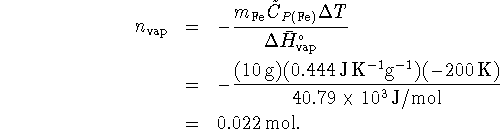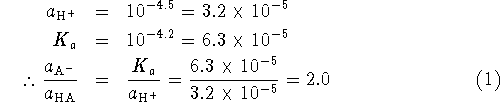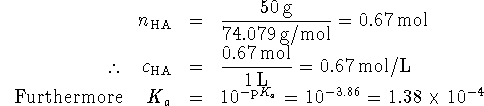
![]() is the equilibrium constant for the dissociation
is the equilibrium constant for the dissociation
![]() .
Since
.
Since ![]() is small, very little of the lactic acid will
dissociate so that
is small, very little of the lactic acid will
dissociate so that ![]() . Also, one
proton is produced for every lactate anion so we have
. Also, one
proton is produced for every lactate anion so we have
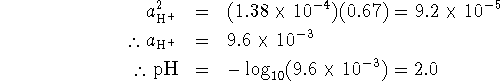
We also want
If we solve equation 1 for ![]() and
substitute this result in equation 2, we get
and
substitute this result in equation 2, we get
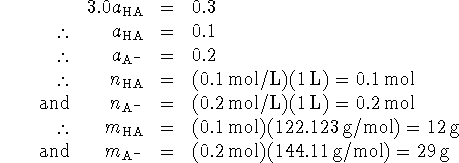
![]()
Thus ![]() .
Since two fluoride ions are liberated for every calcium ion, we
have
.
Since two fluoride ions are liberated for every calcium ion, we
have ![]() . Therefore
. Therefore
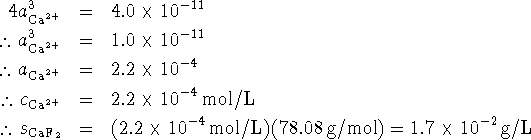
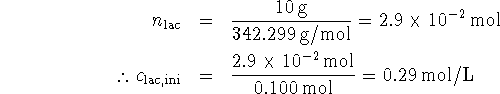
The equilibrium constant is quite large. This implies that almost all of the lactose will have dissociated at equilibrium, leaving us with 0.29mol/L each of glucose and galactose. As for the glucose,
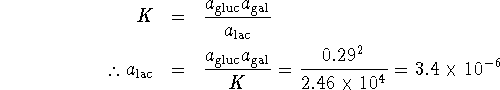
The equilibrium concentration of lactose is therefore ![]() .
.
![]()
where ![]() is the number of moles of water
vaporized. Therefore
is the number of moles of water
vaporized. Therefore