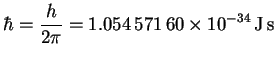
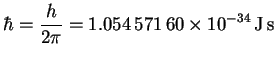
![]()
![]()
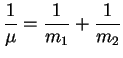
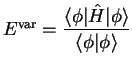
The energy of a system perturbed by an additive Hamiltonian term
![]() can be expressed in the form
E =
E(0) + E(1), where
can be expressed in the form
E =
E(0) + E(1), where
If ![]() and
and ![]() are two angular momentum quantum numbers, the
quantum number for the sum of the associated vectors can take on
any of the following
values:
are two angular momentum quantum numbers, the
quantum number for the sum of the associated vectors can take on
any of the following
values:
If ![]() ,
,
![]() and
and ![]() are arbitrary operators and
k is a constant,
are arbitrary operators and
k is a constant,
![\begin{eqnarray*}[\hat{A},\hat{A}]& = & 0\\
\mbox{}[\hat{A},\hat{B}] & = & -[\h...
...t{C}] & = & \hat{A}[\hat{B},\hat{C}]
+ [\hat{A},\hat{C}]\hat{B}
\end{eqnarray*}](img32.gif)
Terms for ground states of p block elements:
| Configuration | Terms |
| p or p5 |
|
| p2 or p4 |
|
| p3 |
|
For the particle in a box,
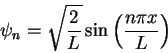
In spherical polar coordinates,
![\begin{eqnarray*}\theta & \in & [0,\pi],\\
\phi & \in & [0,2\pi).
\end{eqnarray*}](img44.gif)
The rotational absorption selection rule is
![]() .
The
rotational energy of a diatomic molecule is given by
.
The
rotational energy of a diatomic molecule is given by
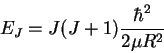
To use ghost atoms in HyperChem: Select the atom you want to turn into a ghost atom. Choose Name Selection from the Select menu. Name the selected atom ``ghost-atoms''. Unselect the atom. Enable ghost atoms in the advanced options dialog of the ab initio setup window. Verify that the charge and multiplicity are correct in the options dialog.