![]()
![]()
The equilibrium constant is related to ![]() by
by
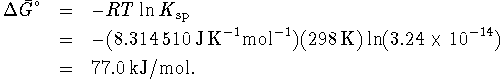
However,
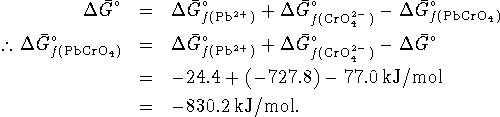
- At the boiling point, the liquid is in equilibrium with
vapor at 1atm. Equilibrium is obtained when
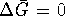 so that
so that
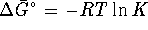 . For this process,
. For this process,
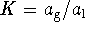 . For the pure liquid,
. For the pure liquid,
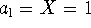 . At the boiling point,
. At the boiling point, 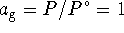 . Therefore
. Therefore 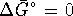 .
However,
.
However, 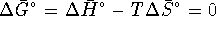 so that
so that

At 298.15K,
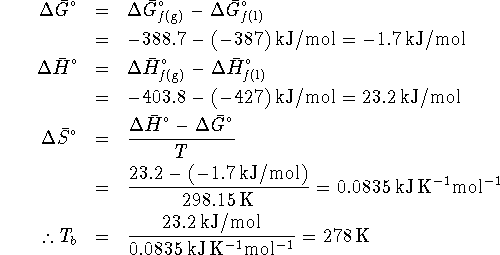
or about
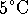 .
. - At 298.15K,
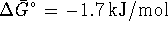 .
Therefore
.
Therefore
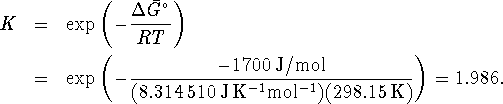
At the boiling point,
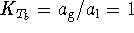 .
Using the relationship between equilibrium constants and
temperatures, we have
.
Using the relationship between equilibrium constants and
temperatures, we have
![]()
The formal (total) acetate concentration in this solution is therefore 0.305mol/L. Acetic acid arises from the reaction
![]()
for which the equilibrium constant is ![]() :
:
![]()
neglecting factors of the standard concentration.
The very small value of ![]() and the significant
initial concentration of acetate together suggest that only a negligible
amount of acetate will react.
It follows that, at equilibrium,
and the significant
initial concentration of acetate together suggest that only a negligible
amount of acetate will react.
It follows that, at equilibrium, ![]() . It follows that
. It follows that
![]()
This product is much larger than ![]() so the
autoionization of water is not significant.
Accordingly, by stoichiometry,
so the
autoionization of water is not significant.
Accordingly, by stoichiometry, ![]() so that
so that
![]()
The activity of ![]() is therefore
is therefore
![]()
which corresponds to a pH of 9.1.
![]()
The standard free energy change for this reaction is
![]()
If ![]() is negative, the reaction is spontaneous.
We can reduce the ratio of ATP to ADP only to the extent that
is negative, the reaction is spontaneous.
We can reduce the ratio of ATP to ADP only to the extent that
![]() remains negative. Beyond that, the reaction is
no longer spontaneous and G6P will not be produced. Thus, the
critical minimum ratio is reached when
remains negative. Beyond that, the reaction is
no longer spontaneous and G6P will not be produced. Thus, the
critical minimum ratio is reached when ![]() , i.e.\
when the reaction is at equilibrium.
, i.e.\
when the reaction is at equilibrium.
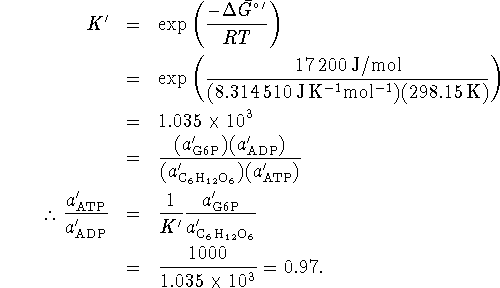
- Step 1:
- The maximum work at 350K is wanted, so this calculation at 298K is not needed.
- Step 2:
- For the reaction as written,
we should have
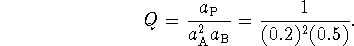
- Steps 2-3:
- The units of
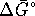 and of the
and of the
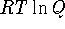 term don't match.
term don't match.
- Steps 5-6:
- This should be a calculation of
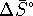 from
from 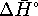 and
and
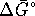 . It is improper to do this
calculation with
. It is improper to do this
calculation with 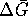 .
.
- Step 6:
- The units of
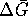 and
and 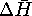 don't match. Also, the sign of
don't match. Also, the sign of 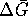 wasn't
properly carried through this calculation. Finally, the
units of
wasn't
properly carried through this calculation. Finally, the
units of 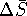 are wrong.
are wrong.
- Step 8:
- The units are again mishandled.
- Step 9:
- Maximum work is
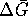 , not
, not
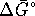 .
.
- Step 10:
- The reaction ratio is again wrong.
- Step 12:
- The free energy change calculated in step
11 is positive so, according to the student's answer, work
must be done on this system for this reaction to
proceed. To be consistent, the student should therefore
report that no work can be obtained.