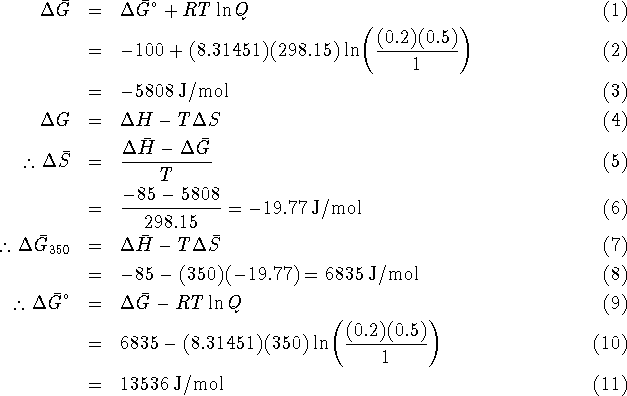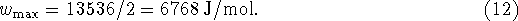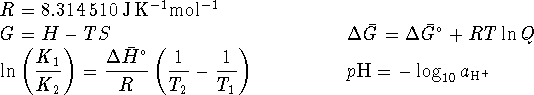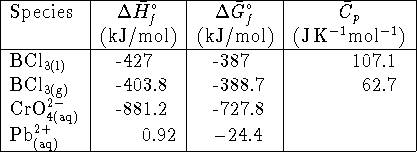Up: Back to the Chemistry 2720 list
of past tests
Chemistry 2720 Fall 1999 Test 2
Answer all questions. Note that useful information (data, equations) is
given at the end of this paper.
Aids allowed: calculator.
- The solubility of lead (II) chromate (
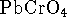 )
in water at 298K is
)
in water at 298K is 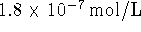 . Calculate the standard
free energy of formation of lead chromate. [10 marks]
. Calculate the standard
free energy of formation of lead chromate. [10 marks] - Estimate the boiling point of
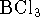 . [10 marks]
. [10 marks] - A sample of 25g of sodium acetate (
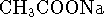 ,
molar mass 82.03g/mol)
is dissolved in 1L of water
at
,
molar mass 82.03g/mol)
is dissolved in 1L of water
at 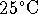 . What is the pH of the solution?
The base ionization constant
(
. What is the pH of the solution?
The base ionization constant
( 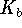 ) of acetate at this temperature
is
) of acetate at this temperature
is 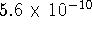 . [10 marks]
. [10 marks]
Hint: 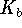 is defined in the information section.
is defined in the information section.
- The synthesis of glucose-6-phosphate (G6P) is a key step in
the biological oxidation of glucose:

This reaction is coupled to ATP hydrolysis:

All data given above correspond to reactions in aqueous solution
at 298.15K.
What is the minimum ratio of ATP to ADP required to maintain a
G6P:glucose ratio of 1000? [10 marks]
Hint: Imagine that conditions are initially such that 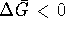 and that the ATP to ADP ratio starts to drop. At what point
does the production of G6P cease to be spontaneous?
and that the ATP to ADP ratio starts to drop. At what point
does the production of G6P cease to be spontaneous?
- Suppose that you are teaching a thermodynamics course. On
one of your tests, you ask the following question:
Calculate the maximum non-PV work which can be obtained from the
reaction
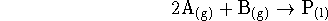
per mole of A reacted at 350K when the partial pressures of A and B are,
respectively, 0.2 and 0.5atm.
For this reaction, 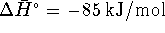 and
and 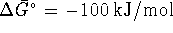 at 298.15K.
at 298.15K.
One student's solution goes as follows:
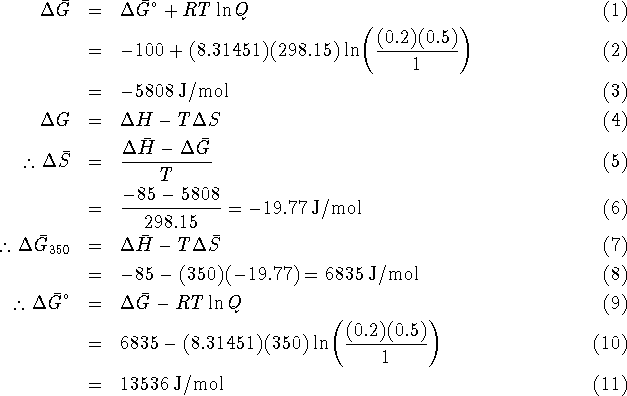
Since the reaction involves two equivalents of A,
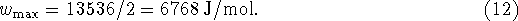
Identify and briefly explain the errors in the student's
solution. Refer to steps of the student's solution by number.
[10 marks]
The autoionization constant of water ( 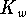 ) at 298.15K is
) at 298.15K is 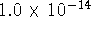 .
.
The base ionization constant 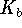 is the equilibrium constant for the
reaction
is the equilibrium constant for the
reaction
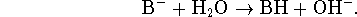
To convert degrees Celsius to Kelvin, add 273.15.
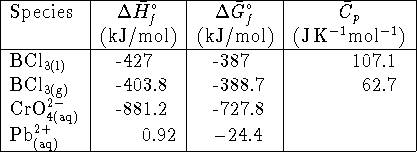

Up: Back to the Chemistry 2720 list
of past tests
Marc Roussel
Thu Nov 18 11:07:30 MST 1999
![]() is defined in the information section.
is defined in the information section.![]()
![]()
![]() and that the ATP to ADP ratio starts to drop. At what point
does the production of G6P cease to be spontaneous?
and that the ATP to ADP ratio starts to drop. At what point
does the production of G6P cease to be spontaneous?
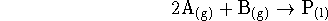
and
at 298.15K.