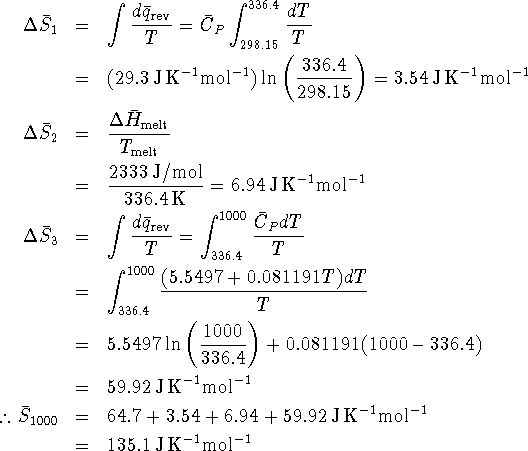- False. The first law only forbids energy
nonconservation. Melting ice below
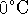 (forming
supercooled water) is allowed by the first law. It is only
disallowed by the second law.
(forming
supercooled water) is allowed by the first law. It is only
disallowed by the second law. - True
- True
- True
- False. The enthalpy of formation of a hydrogen ion is arbitrarily set to be zero, which makes the enthalpies of formation of other aqueous ions measurable.
- True
- False. The
 of a reaction
in and of itself tells us nothing about whether the reaction is
spontaneous. To decide whether a reaction is spontaneous or
not, we need to know
of a reaction
in and of itself tells us nothing about whether the reaction is
spontaneous. To decide whether a reaction is spontaneous or
not, we need to know  for the Universe (or at least
for an approximately adiabatic subset thereof) and not just for
a reaction.
for the Universe (or at least
for an approximately adiabatic subset thereof) and not just for
a reaction.
![]()
Coal releases 25kJ/g, so
![]()
- During a reversible expansion,
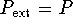 .
Therefore
.
Therefore 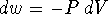 . For an ideal gas,
PV = nRT so we have
. For an ideal gas,
PV = nRT so we have
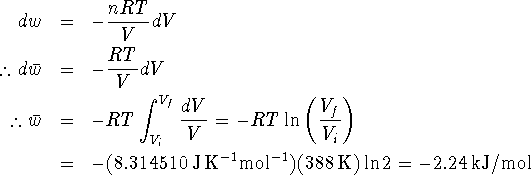
- No process can produce more work than an equivalent reversible process. The claim that the machine produces 3.5kJ/mol is in error. Your friend shouldn't invest.
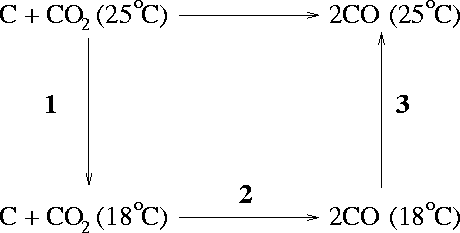
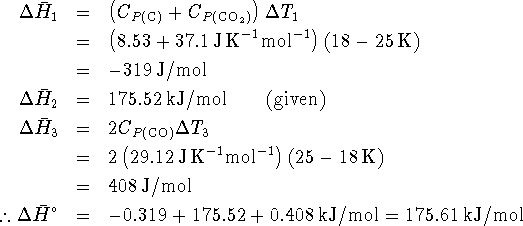
The enthalpy of reaction is related to the enthalpies of reaction by
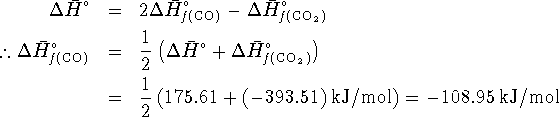
![]()
We just need to calculate the entropy change for each of the steps and add this to the entropy of the solid at 298.15K to get the desired entropy.