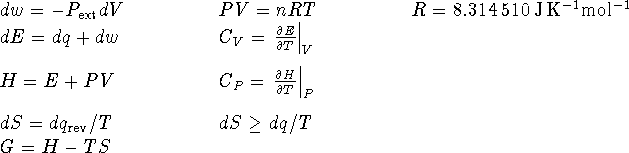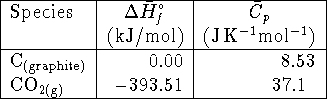- The first law forbids the melting of ice below
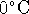 at atmospheric pressure.
at atmospheric pressure. - Since E is a state function, then for any process which
returns the system to its original state (a cyclic
process)
 .
. - If
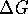 for a reaction at constant temperature
and pressure is negative, the reaction
is spontaneous.
for a reaction at constant temperature
and pressure is negative, the reaction
is spontaneous. - The second law limits the efficiency of the conversion of heat into work but does not limit the conversion of work into heat.
- The enthalpy of formation of an aqueous hydrogen ion is a measurable quantity.
- The entropy of the universe never decreases.
- If
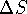 for a reaction is negative, the reaction
is not spontaneous.
for a reaction is negative, the reaction
is not spontaneous.
- Calculate the work done per mole
when an ideal gas is expanded reversibly by a
factor of 2 at
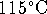 .
[7 marks]
.
[7 marks] - A friend thinking of investing in a company which
makes engines shows you the company's prospectus.
Analyzing the machine, you realize that it
works by harnessing the expansion of a gas. The
machine's operating temperature is approximately
constant at
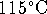 and the
gas doubles in volume during the power extraction phase
of operation. A
quick calculation shows that the machine is claimed to
produce about 3.5kJ/mol of work during the expansion.
What advice would you give your friend? Give a brief
thermodynamic rationale.
[3 marks]
and the
gas doubles in volume during the power extraction phase
of operation. A
quick calculation shows that the machine is claimed to
produce about 3.5kJ/mol of work during the expansion.
What advice would you give your friend? Give a brief
thermodynamic rationale.
[3 marks]
![]()
is ![]() .
The specific heat capacity of carbon monoxide is
.
The specific heat capacity of carbon monoxide is ![]() .
Accurately calculate the standard enthalpy
of formation of carbon monoxide (at
.
Accurately calculate the standard enthalpy
of formation of carbon monoxide (at ![]() ).
[10 marks]
).
[10 marks]
![]()
where ![]() is in
is in ![]() and T is
in Kelvin.
The entropy of solid potassium at 298.15K is
and T is
in Kelvin.
The entropy of solid potassium at 298.15K is ![]() . What is the entropy of liquid potassium at 1000K?
[10 marks]
. What is the entropy of liquid potassium at 1000K?
[10 marks]