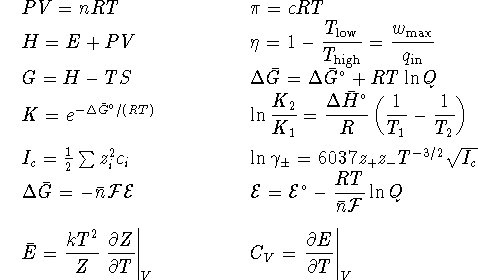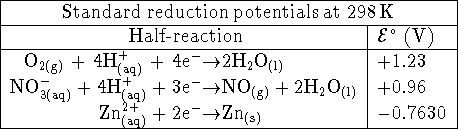You have three hours to complete this exam. You may not leave the
examination hall in the first hour or in the last 10 minutes.
The aggregate value of all questions on this exam is 100.
Your answers must be recorded in the exam booklets provided. Please
note the useful information at the end of the paper.
- Calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction
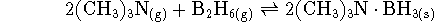
at 298K. [5 marks]
- Pyruvate ions (
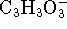 ) react with
glucose (
) react with
glucose ( 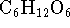 ). The unbalanced
half-reactions are
). The unbalanced
half-reactions are
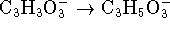 and
and 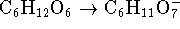 .
The
reaction medium is slightly acidic. Balance the
reaction. [5 marks]
.
The
reaction medium is slightly acidic. Balance the
reaction. [5 marks] - Carbohydrates have the empirical formula
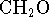 .
Show that for the combustion of carbohydrates
in a calorimeter
.
Show that for the combustion of carbohydrates
in a calorimeter 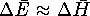 .
Hint: The temperature in a calorimeter seldom rises
very far above room temperature. At these temperatures,
carbohydrates are solids and water is liquid. [4 marks]
.
Hint: The temperature in a calorimeter seldom rises
very far above room temperature. At these temperatures,
carbohydrates are solids and water is liquid. [4 marks] - A typical adult male human must consume food with an energy
equivalent of about 3000kcal/day to maintain a constant
weight.
Assume that the food energy is completely converted to
heat and, furthermore, that the heat is generated at a
constant rate during the day.
The human body is mostly water (specific heat capacity
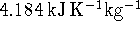 ). If the body were
perfectly insulated,
how long would it take
before a 70kg adult male reached the normal boiling
point of water from an
initial temperature of
). If the body were
perfectly insulated,
how long would it take
before a 70kg adult male reached the normal boiling
point of water from an
initial temperature of 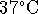 ?
[6 marks]
?
[6 marks] - A key reaction in the synthesis of fats in living organisms is
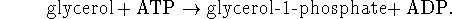
The ratio of ATP to ADP is held fixed at a value of 10 by
homeostatic mechanisms. The maximum observed
ratio of glycerol-1-phosphate
to glycerol is 770 at 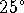 C.
C. 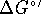 for
ATP hydrolysis
for
ATP hydrolysis
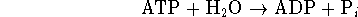
is -31.0kJ/mol at 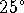 C. What is
C. What is 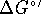 for the direct reaction of glycerol with phosphate? [10 marks]
for the direct reaction of glycerol with phosphate? [10 marks]
- Ribonuclease has two conformations, only one of which is active.
A solution containing 1mmol/L of ribonuclease is prepared.
At
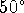 C, the equilibrium concentrations of the active
and inactive forms are, respectively,
C, the equilibrium concentrations of the active
and inactive forms are, respectively,
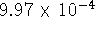 and
and 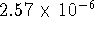 mol/L.
At
mol/L.
At 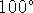 C, the equilibrium concentrations of the active and
inactive forms are
C, the equilibrium concentrations of the active and
inactive forms are 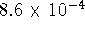 and
and 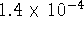 mol/L.
What is
mol/L.
What is 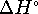 for the process which converts
the active form to its inactive conformation? [10
marks]
for the process which converts
the active form to its inactive conformation? [10
marks] - An electrical generator is a heat engine. Suppose that a
generator burns ethanol at a rate of 10L/h. The generator's
combustion chamber runs at
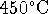 and the
temperature of the exhaust
manifold is
and the
temperature of the exhaust
manifold is 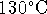 . What is the maximum
electrical power (measured in
W, i.e. in J/s) which such a generator might produce? The
density of ethanol is 790g/L and its molar mass is
46.069g/mol. [10 marks]
. What is the maximum
electrical power (measured in
W, i.e. in J/s) which such a generator might produce? The
density of ethanol is 790g/L and its molar mass is
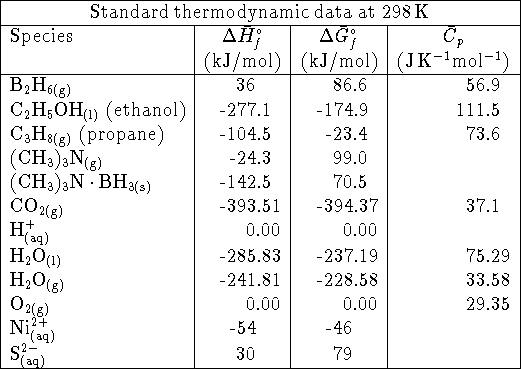
46.069g/mol. [10 marks] - The solubility of nickel (II) sulfide in water at 298K is
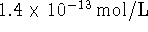 . What is the standard free energy
of formation of solid nickel (II) sulfide? [10 marks]
. What is the standard free energy
of formation of solid nickel (II) sulfide? [10 marks] - Many enzymes exist in solution as multimers,
i.e. they assemble
into
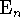 complexes:
complexes:

These multimers are held together by weak intermolecular forces.
Suppose that the molar mass of a
certain enzyme has been determined to be 120kg/mol
from crystal structure data. A solution of 8.00g of enzyme in
100mL of water is prepared. The osmotic pressure of this
solution is 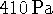 at 298K. Does this enzyme
form multimers in solution? If so, what is the number
of enzyme molecules in each complex? [10 marks]
at 298K. Does this enzyme
form multimers in solution? If so, what is the number
of enzyme molecules in each complex? [10 marks]
- The following cell is operated in Lethbridge at 298K:
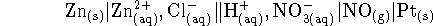
The concentration of zinc chloride in the left half-cell is
0.002mol/L. The right half-cell contains 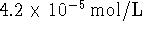 nitric acid. Bubbles of nitrogen
monoxide form on the inert platinum electrode. The pressure of
NO in these bubbles is approximately 0.9atm (the ambient
atmospheric pressure at our altitude). Assume that the NO gas
behaves ideally.
Calculate the voltage produced by this cell using Debye-Hückel
theory. [10 marks]
nitric acid. Bubbles of nitrogen
monoxide form on the inert platinum electrode. The pressure of
NO in these bubbles is approximately 0.9atm (the ambient
atmospheric pressure at our altitude). Assume that the NO gas
behaves ideally.
Calculate the voltage produced by this cell using Debye-Hückel
theory. [10 marks]
-
- Propane is a gas at room temperature.
A fuel cell operates on propane at a pressure of 1atm
at 298K. Assume that
propane is an ideal gas and calculate the maximum
electrical
work available from the fuel cell per cubic metre of
propane oxidized if the oxygen pressure is 0.2atm and
the carbon dioxide pressure is 0.03atm.
Hint: Calculate the maximum work per mole first.
[7 marks]
- Calculate the voltage produced by the fuel cell under the
operating conditions described above. [3 marks]
- At reasonable temperatures, the noble gases behave like structureless
spherical particles all of whose energy is translational kinetic
energy, i.e. they behave like ideal gases.
The partition function for particles which have only
kinetic energy is
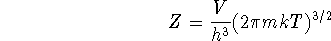
where V is the volume of the container in which the gas is
held, h is Planck's constant,  , m is
the mass of the particles (atoms),
k is Boltzmann's constant and T is the
temperature.
Calculate the constant volume specific heat capacity
of an ideal gas.
Compare your answer to the experimental
value of
, m is
the mass of the particles (atoms),
k is Boltzmann's constant and T is the
temperature.
Calculate the constant volume specific heat capacity
of an ideal gas.
Compare your answer to the experimental
value of 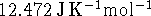 .
Hint: The
identity
.
Hint: The
identity 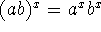 may be useful.
[10 marks]
may be useful.
[10 marks]
To convert degrees Celcius to Kelvin, add 273.15.
![]()
![]()
![]() C.
C. ![]() for
ATP hydrolysis
for
ATP hydrolysis
![]()
![]() C. What is
C. What is ![]() for the direct reaction of glycerol with phosphate? [10 marks]
for the direct reaction of glycerol with phosphate? [10 marks]![]()
![]() at 298K. Does this enzyme
form multimers in solution? If so, what is the number
of enzyme molecules in each complex? [10 marks]
at 298K. Does this enzyme
form multimers in solution? If so, what is the number
of enzyme molecules in each complex? [10 marks]![]()
![]() nitric acid. Bubbles of nitrogen
monoxide form on the inert platinum electrode. The pressure of
NO in these bubbles is approximately 0.9atm (the ambient
atmospheric pressure at our altitude). Assume that the NO gas
behaves ideally.
Calculate the voltage produced by this cell using Debye-Hückel
theory. [10 marks]
nitric acid. Bubbles of nitrogen
monoxide form on the inert platinum electrode. The pressure of
NO in these bubbles is approximately 0.9atm (the ambient
atmospheric pressure at our altitude). Assume that the NO gas
behaves ideally.
Calculate the voltage produced by this cell using Debye-Hückel
theory. [10 marks]![]()
![]() , m is
the mass of the particles (atoms),
k is Boltzmann's constant and T is the
temperature.
Calculate the constant volume specific heat capacity
of an ideal gas.
Compare your answer to the experimental
value of
, m is
the mass of the particles (atoms),
k is Boltzmann's constant and T is the
temperature.
Calculate the constant volume specific heat capacity
of an ideal gas.
Compare your answer to the experimental
value of ![]() .
Hint: The
identity
.
Hint: The
identity ![]() may be useful.
[10 marks]
may be useful.
[10 marks]