- (a)
- d corresponds to
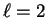 ,
so the possible values of
,
so the possible values of
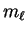 are
-2,-1,0,1,2. Thus, there are five of
these.
are
-2,-1,0,1,2. Thus, there are five of
these.
- (b)
- For n=3,
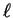 can't be any larger than 2. However,
f orbitals correspond to
can't be any larger than 2. However,
f orbitals correspond to 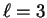 so there are in fact
no 3f orbitals.
so there are in fact
no 3f orbitals.
- Photoelectric effect: Due to the relationship between the energy and frequency of photons, light of too low a frequency cannot cause the ejection of electrons from metals. The intensity (brightness) of the light is relevant only insofar as additional photons can cause more ejections, but only if the individual photons have enough energy.
- Electron/neutron diffraction: Particles (such as electrons) have wave properties so that they can diffract through matter.
- Spectroscopy: Quantum systems generally have discrete energy levels. As a result, they can absorb or emit radiation only at certain wavelengths.
- Tunneling: Quantum mechanical particles can be transmitted through energy barriers which, classically, they would not be able to surpass.
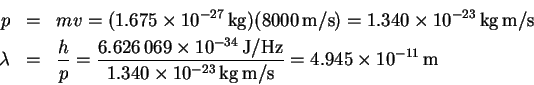
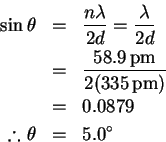
- (a)
- We start from the uncertainty principle
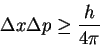
and note that
E = cp
for massless particles. Therefore
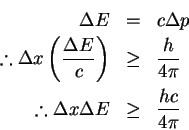
- (b)
- Using the inequality derived above, we have
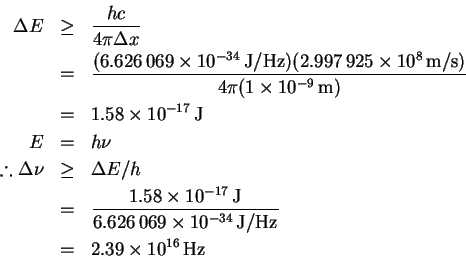
This is enormous, considering that optical frequencies are in the range of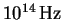 .
.
EI = -E1 = Z2RH.
Our task is to solve this equation for Z. First, we must convert the ionization energy to Joules:
Thus we have
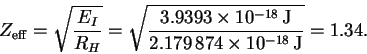
This value is less than 2 because the electron which remains after ionization shields the removed electron from the full nuclear charge.
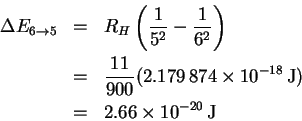
The frequency is
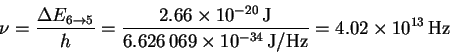
The corresponding wavelength is
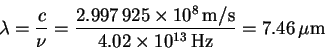
The others are computed analogously. Here are the results:
| ni |
|
| 6 | 7.46 |
| 7 | 4.65 |
| 8 | 3.74 |
| 9 | 3.30 |
- (a)
- We first want to calculate the minimum (kinetic) energy from the
particle-in-a-box formula:
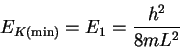
We need the mass of a single protein molecule:
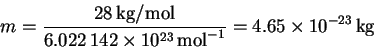
Thus,
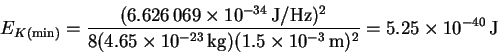
We use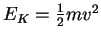 to calculate a minimum speed:
to calculate a minimum speed:
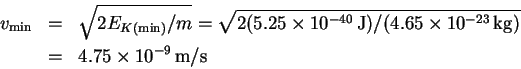
- (b)
- The average kinetic energy at room temperature is
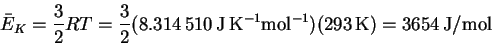
On a per molecule basis, this is
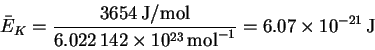
This is enormously larger than the minimum imposed by quantum mechanics, so quantum effects are of no particular significance in this system.