The order with respect to C is easiest to determine: The rate goes down by a factor of 10 every time the concentration of C goes down by a factor of 10 (experiments 1, 4 and 5). The rate is therefore proportional to the first power of c.
For A, consider the following table:
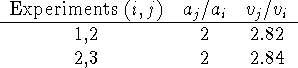
Thus, the rate goes up by a factor of about 2.83 when the concentration is doubled. We are looking for a simple rate law of the form
![]()
Ratios of rates at constant c are therefore related by
![]()
By taking logarithms of both sides of this equation, we get
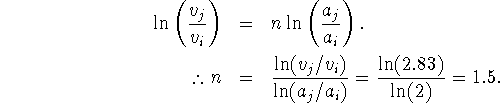
The rate law is therefore
![]()
The rate constant can be found using the data from any of the experiments. For instance, using experiment 1, we get
![]()