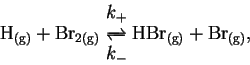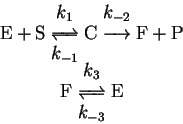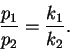Up: Back to the Chemistry 2710 test
index
Chemistry 2710 Spring 2000 Final Examination
Name:
Aids allowed: calculator, one
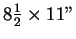 sheet of notes
sheet of notes
If you have a graphing calculator,
you can use it rather than hand drawing graphs. If you do use your
calculator's graphing capabilities, explain in
detail what you did (what graphs you drew, how you interpreted them,
etc.). If you need to draw graphs by hand, graph paper is included at
the end of this exam. Make sure to label your graphs with
the question number.
- Useful data:
-
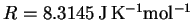 ,
,
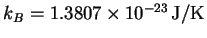 ,
,
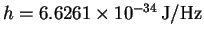 .
.
At 298.15K,
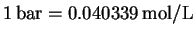 .
.
To convert degrees Celsius to Kelvin, add 273.15.
- 1.
- The rate of a reaction triples when the concentration of a
reactant is doubled. What is the order of the reaction with
respect to the concentration of this reactant?
[4 marks]
- 2.
- Explain briefly the physical meaning of the exponential term
in the Arrhenius formula.
[4 marks]
- 3.
- A set of initial velocity experiments was performed for the reaction
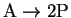 by stopping the reaction
after approximately 1min and measuring the
concentration of P (initially zero).
In one run, the initial concentration of A
was 0.04mol/L. The reaction was stopped at 64s, at which
time p had reached
by stopping the reaction
after approximately 1min and measuring the
concentration of P (initially zero).
In one run, the initial concentration of A
was 0.04mol/L. The reaction was stopped at 64s, at which
time p had reached
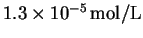 .
What was the initial rate? [4 marks]
.
What was the initial rate? [4 marks]
- 4.
- Find the reactions in the following list which are either
certainly or probably not elementary and explain briefly which
features make it so. [4 marks]
- (a)
-
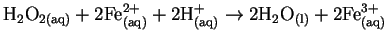
- (b)
-
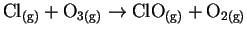
- (c)
-
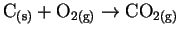
- 5.
- The rate constant for the reaction of hydroxyl radicals with
methanal (formaldehyde) has been measured as a function of
temperature:
| T (K) |
k (
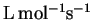 ) ) |
| 250 |
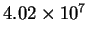 |
| 286 |
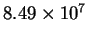 |
| 333 |
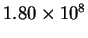 |
| 400 |
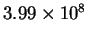 |
| 500 |
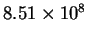 |
| 667 |
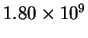 |
Calculate the activation energy and preexponential factor
for this reaction. [10 marks]
- 6.
- Methyl radicals react with ethane to form methane and ethyl
radicals:
The preexponential factor for this elementary reaction is
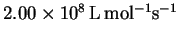 .
What is the entropy of
activation at 298.15K? What does the value of the entropy of
activation of this reaction tell you about the transition state?
[8 marks]
.
What is the entropy of
activation at 298.15K? What does the value of the entropy of
activation of this reaction tell you about the transition state?
[8 marks]
- 7.
- Suppose that a certain drug is administered in pill form at a
rate of one pill every 6 hours. Each pill, as it is manufactured,
contains 18mg of the drug. The minimum effective dose for an
adult of average mass is
12mg every 6 hours. The drug is somewhat unstable and breaks
down in a pseudo-first-order reaction with a half-life of
47days.
What is the shelf life of the drug? In other words, how long
does it take before each pill contains less than the minimum
effective dose? [5 marks]
- 8.
- The empirical rate law for the reaction of aniline with iodine
is
v = k[aniline][I2].
The reaction is followed by withdrawing 10mL aliquots of the reaction
mixture at roughly equal time intervals. These aliquots are
titrated with thiosulfate solution to determine the iodine
concentration. The reaction of iodine with thiosulfate is
- (a)
- What is the integrated rate law if the initial
concentrations of iodine and aniline are equal?
Express your answer in terms of the concentration of
iodine. [2 marks]
Note: It is not necessary to show the derivation.
- (b)
- The following titration data were obtained in one run
with
![$\mathrm{[aniline]}_0 = \mathrm{[I_2]}_0 =
0.0040\,\mathrm{mol/L}$](img22.gif) and
and
![$\mathrm{[S_2O_3^{2-}]} =
0.0100\,\mathrm{mol/L}$](img23.gif) :
:
| t (min) |
V (mL) |
| 0.00 |
7.23 |
| 10.25 |
5.85 |
| 20.60 |
5.03 |
| 29.85 |
4.40 |
| 40.11 |
3.90 |
| 49.63 |
3.51 |
| 59.88 |
3.21 |
| 70.69 |
2.94 |
| 80.80 |
2.66 |
Calculate the rate constant for the reaction. [10 marks]
- 9.
- For the elementary reaction
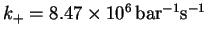 and the
equilibrium constant
and the
equilibrium constant
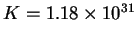 at 298.15K.
What is the value of k-? [4 marks]
at 298.15K.
What is the value of k-? [4 marks]
- 10.
- In enzyme reactions, it is not uncommon for the enzyme to be left
in an unreactive conformation after release of the product. A
subsequent reaction converts the enzyme back to the active form.
Symbolically, the mechanism is
where E is the active form of the enzyme and F its inactive form,
S is the substrate, P the product, and C the enzyme-substrate complex.
Derive the rate law for this mechanism using the steady-state and/or
equilibrium approximations, as appropriate.
Is this mechanism kinetically distinguishable from the Michaelis-Menten
mechanism? [10 marks]
- 11.
- Briefly describe how you can recognize competitive inhibition
of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction using Eadie-Hofstee plots.
[5 marks]
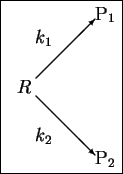
- 12.
- In class, we found that the product ratio for parallel first-order
reactions
is just
The product ratio of course varies with T since both k1 and
k2 vary with T.
Suppose that at
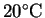 ,
p1/p2 = 20 while at
,
p1/p2 = 20 while at
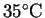 ,
p1/p2 = 15.
What is the difference in the activation energies of
the two reactions? Make sure that your answer makes it
clear which of the two reactions has the higher
activation energy. [10 marks]
,
p1/p2 = 15.
What is the difference in the activation energies of
the two reactions? Make sure that your answer makes it
clear which of the two reactions has the higher
activation energy. [10 marks]
- 13.
- Create your own kinetics question and provide an answer for it.
You should try to create a question of a similar level
of difficulty as questions worth 10 marks on this exam.
In other words, your question should require a few solution steps.
If the question is in parts, the parts should be intimately
interrelated.
Moreover, your question
should be substantially different from any other question on
this exam.
Your question will be judged on the following points:
- Appropriate level of difficulty
- Originality: The question tests different concepts
than those covered by other questions in this exam.
- Correctness: The question and associated solution do not
contain any conceptual
or technical errors.
- Completeness: The question contains all data necessary for
its solution. All necessary solution steps are shown.
- Clarity: The question and solution are clearly
understandable.
It may be a good idea to rough out your question on
scrap paper before writing down the final version.
[20 marks]



Up: Back to the Chemistry 2710 test
index
Marc Roussel
2000-04-27
![]() sheet of notes
sheet of notes