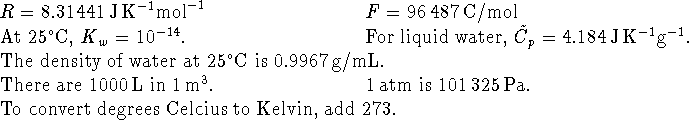- If a reaction has a rate-determining step
 what is the order
of the reaction with respect to B?
what is the order
of the reaction with respect to B? - A living cell placed in distilled water bursts. Why?
- Which is higher:
The vapour pressure of pure water at
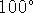 C or the vapour pressure of a sodium chloride
solution at
C or the vapour pressure of a sodium chloride
solution at 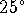 C?
C? - Give three different ways you can use to decide whether or not a reaction is spontaneous.
- Does the equilibrium constant of an exothermic process increase or decrease with temperature?
- What are the three conditions for the production of electricity by a chemical reaction?
- For the reaction
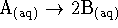 ,
, 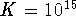 and the initial
concentration of A is 1mol/L. What is the equilibrium
concentration of B?
and the initial
concentration of A is 1mol/L. What is the equilibrium
concentration of B? - What is the pH of a 0.02mol/L sodium hydroxide
solution at
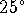 C?
C? - A solution of oxalic acid
(H
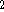 C
C 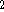 O
O 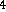 ) is mixed with
a hydrogen peroxide (H
) is mixed with
a hydrogen peroxide (H 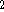 O
O 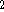 )
solution. A redox reaction occurs and carbon dioxide bubbles
out. Balance the reaction.
)
solution. A redox reaction occurs and carbon dioxide bubbles
out. Balance the reaction. - What is the entropy change in the reaction
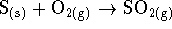 ?
? - For the reaction
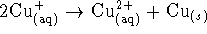 ,
,
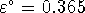 V. What is
V. What is 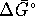 ?
?
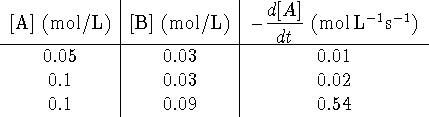
- What is the experimental rate equation for [A]?
- Calculate the rate constant.
- What is the pH of the solution at equilibrium?
- If the HCl solution
starts at
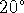 C, what is the
final temperature?
C, what is the
final temperature?
![]()
is a reasonable guess. The reaction generates the products in stoichiometric quantities.
- A 200g sample of lead (II) azide explodes.
Its initial temperature is
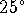 C. Suppose that
all of the heat liberated by the reaction is held in the
products. (This is a reasonable approximation when a
chemical reaction occurs quickly. The heat just doesn't
have time to get away.) What is the final temperature
of the products?
C. Suppose that
all of the heat liberated by the reaction is held in the
products. (This is a reasonable approximation when a
chemical reaction occurs quickly. The heat just doesn't
have time to get away.) What is the final temperature
of the products? - What is the volume of gas produced at 1atm? Express your answer in litres.
- Calculate the vapour pressure of pure pentane at
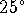 C.
C. - If 10g of dodecane (C
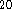 H
H 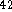 , molar mass
282.552g/mol) is dissolved in 30g of pentane (molar
mass 72.150g/mol), what is the vapour pressure of the
solution? Note that dodecane has a much lower
vapour pressure than pentane.
, molar mass
282.552g/mol) is dissolved in 30g of pentane (molar
mass 72.150g/mol), what is the vapour pressure of the
solution? Note that dodecane has a much lower
vapour pressure than pentane.
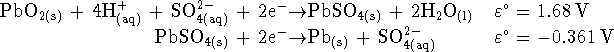
- What is the overall reaction when the battery is producing electricity?
- Calculate the voltage
produced by this battery
when the sulphuric acid
concentration is 2mol/L at
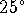 C.
C.
![]()
is 0.534. If 0.2atm of H ![]() and 0.8atm of CO
and 0.8atm of CO ![]() are mixed
in a rigid container, what are the equilibrium pressures of the
four gases?
are mixed
in a rigid container, what are the equilibrium pressures of the
four gases?