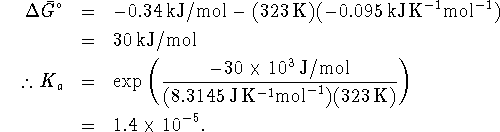- This is a heat balance problem. Since there is no indication
to the contrary, we must assume that no heat is either gained or
lost by the system (wood+water).
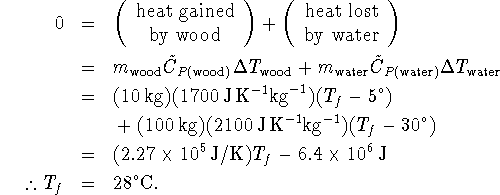
Note that the answer comes out in  because we
set up the problem using temperatures in these units.
because we
set up the problem using temperatures in these units.
- This is another heat balance problem, this one involving latent
heat.
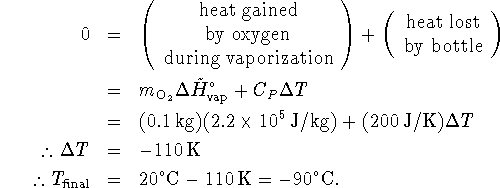
- From
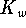 , we can calculate
, we can calculate 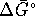 for the
reaction.
for the
reaction.
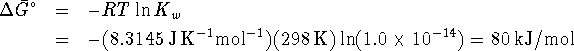
However
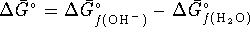 (since the
standard free energy of formation of an aqueous proton is zero)
so that
(since the
standard free energy of formation of an aqueous proton is zero)
so that
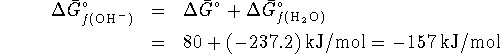
- For the process
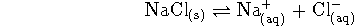
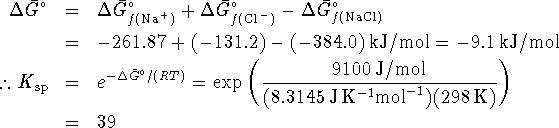
This is a very large 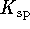 so it agrees with the usual
rule about the solubility of alkali metal salts.
so it agrees with the usual
rule about the solubility of alkali metal salts.
- At the boiling point, the liquid and gas are in equilibrium so,
for the process
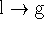 ,
,
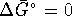 . (We can use
. (We can use 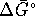 instead of
instead of 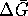 because we are considering a pure
solvent and the normal boiling point is taken at 1atm of
pressure, which is the standard gas pressure.)
That being the case,
because we are considering a pure
solvent and the normal boiling point is taken at 1atm of
pressure, which is the standard gas pressure.)
That being the case, 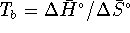 .
.
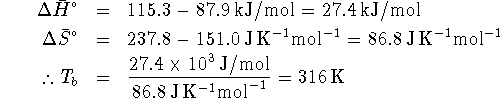
or, in degrees Celcius, 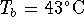 .
.
- The reaction involves the breaking of two C-Br bonds (one per
bromomethane molecule) and of an F-F bond and the making of two
C-F bonds and of a Br-Br bond. Therefore
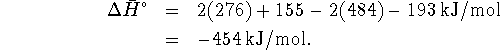
- From the equilibrium constant, we can calculate
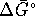 :
:
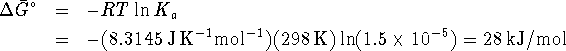
Given 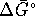 and
and 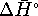 , we can
calculate
, we can
calculate 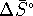 :
:
At 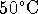 (323K),
(323K),
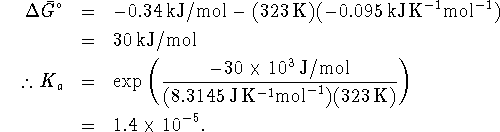
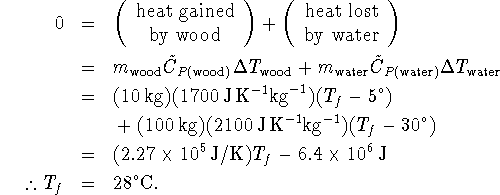
![]() because we
set up the problem using temperatures in these units.
because we
set up the problem using temperatures in these units.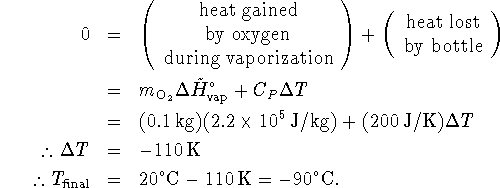
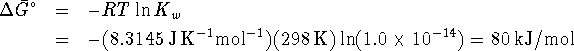
![]() (since the
standard free energy of formation of an aqueous proton is zero)
so that
(since the
standard free energy of formation of an aqueous proton is zero)
so that
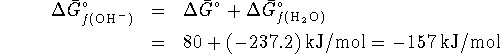
![]()
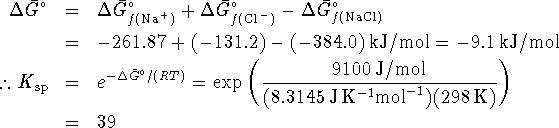
![]() so it agrees with the usual
rule about the solubility of alkali metal salts.
so it agrees with the usual
rule about the solubility of alkali metal salts.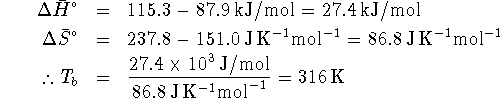
![]() .
.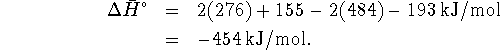
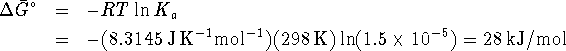
![]() and
and ![]() , we can
calculate
, we can
calculate ![]() :
:
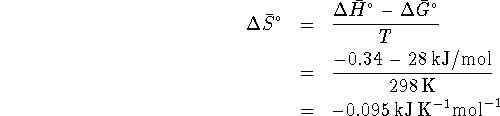
![]() (323K),
(323K),