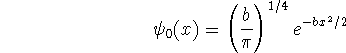
where ![]() is a constant.
Report your answer in terms of
is a constant.
Report your answer in terms of ![]() and
and ![]() . Compare the average kinetic energy to the
total energy of the oscillator. [10 marks]
. Compare the average kinetic energy to the
total energy of the oscillator. [10 marks]
Maple notes:
The number ![]() is Pi in Maple. The function
is Pi in Maple. The function ![]() is
called exp(x) in Maple. It's easier to do the
calculation in terms of b and then to substitute the value of
b in by hand at the end than it is to do this problem any other way.
Use
is
called exp(x) in Maple. It's easier to do the
calculation in terms of b and then to substitute the value of
b in by hand at the end than it is to do this problem any other way.
Use
assume(b>0);
to tell Maple that b is a positive number. You may find it
useful to run your answer through the simplify()
function before doing any further work with it.
![]()
where ![]() is a constant and
is a constant and ![]() is the
displacement of the bond from its equilibrium length.
is the
displacement of the bond from its equilibrium length.![]() Use the trial wavefunction
Use the trial wavefunction
![]()
Find the best value of b and the best energy obtainable for
wavefunctions of this form. Normalize the wavefunction.
Express the energy in terms of ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() but
leave the normalization factor in terms of b.
[15 marks]
but
leave the normalization factor in terms of b.
[15 marks]
Mathematical note: The equation used to find the best value of b may have several solutions. Only solutions whose real part is positive are physically admissible.
Maple notes: Maple will need to be helped out to solve this
problem. Type
assume(b>0);
into your Maple session before attempting to solve this problem.
Use simplify() to get the energy into a simple form after
computing it.
At one stage of the problem,
Maple will probably return a list of solutions (separated by
commas). Only one is physically reasonable.
It may be necessary for you to do some work (e.g. substitutions)
by hand.