- (a)
- Describe the electron correlation problem in the context of SCF calculations. [5 marks]
- (b)
- Briefly describe two computational methods by which electron correlation can be treated. [4 marks]
- (c)
- When calculating
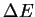 's, in what kinds of reactions are
correlation effects likely to be important? In what
kinds of reactions is correlation unimportant?
[4 marks]
's, in what kinds of reactions are
correlation effects likely to be important? In what
kinds of reactions is correlation unimportant?
[4 marks]
- (d)
- Provide a specific example of a reaction in which correlation is unimportant. Support your example with a HyperChem calculation. [10 marks]
- (e)
- Provide a specific example of a reaction in which
correlation has a material effect on the
computed
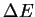 .
Support your example with
a HyperChem calculation.
[10 marks]
.
Support your example with
a HyperChem calculation.
[10 marks]
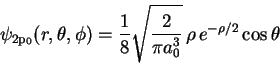
where
Maple hints: ![]() is Pi in Maple,
is Pi in Maple, ![]() is
sqrt(u), and eu is
exp(u). Maple will need to know that a0>0.
is
sqrt(u), and eu is
exp(u). Maple will need to know that a0>0.
Obtain an equation for the energy levels of a particle in a box which includes the relativistic correction. Reduce all instances of
Hints: This question can be answered without explicitly evaluating any
integrals. However, if you do apply the formal procedure, you will
need to tell Maple that the quantum number is an integer.
Recall also that ![]() is spelled Pi in Maple and that
is spelled Pi in Maple and that
![]() is sqrt(u).
is sqrt(u).
- (a)
- A diatomic molecule with a reduced mass of
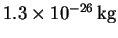 has an effective potential energy
curve approximately given by
has an effective potential energy
curve approximately given by
![\begin{displaymath}V_\mathrm{eff}(R) = A\left[\left(\frac{B}{R}\right)^2
- \frac{B}{R}\right]\end{displaymath}](img9.gif)
where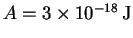 and
and
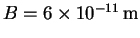 .
Find the equilibrium bond length and potential
energy at equilibrium.
[5 marks]
.
Find the equilibrium bond length and potential
energy at equilibrium.
[5 marks]
- (b)
- Using the trial wavefunction
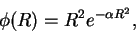
estimate the ground-state energy. [10 marks]Maple hints: Maple will need to know that
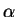 is
a positive parameter. Enter numeric values for all
constants and parameters before carrying out any
mathematical operations. Don't forget that eu is
exp(u) in Maple. Use assign()
to set
the value of the variational parameter at the end of the
computation.
Syntax:
assign(u=a);sets the value of variable u to a.
is
a positive parameter. Enter numeric values for all
constants and parameters before carrying out any
mathematical operations. Don't forget that eu is
exp(u) in Maple. Use assign()
to set
the value of the variational parameter at the end of the
computation.
Syntax:
assign(u=a);sets the value of variable u to a. - (c)
- Find the location of the maximum of the wavefunction. Comment on the quality of the variational wavefunction. [5 marks]
- (d)
- Estimate the dissociation energy.
[2 marks]
Hint: What is
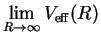 ?
?
- (e)
- What could you do to improve the accuracy of these calculations? [2 marks]