


Up: Back to the Chemistry 2720 test index
Chemistry 2720 Fall 2000 Test 2
Formulas and data can be found at the end of this paper.
Write your answers only in the booklet provided. Use extra pages at the
back of the booklet for scratch work.
- 1.
- State the number of orbitals of each of the following types which an
atom can have: [4 marks]
- (a)
- 5d
- (b)
- 3f
- 2.
- Briefly describe two phenomena which are explained by quantum
mechanics but not by classical mechanics. [4 marks]
- 3.
- What is the wavelength associated with a neutron (
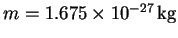 )
whose speed
is 8000m/s?
[4 marks]
)
whose speed
is 8000m/s?
[4 marks]
- 4.
- Recall that graphite is made up of sheets of fused six-membered
carbon rings. These sheets are 335pm apart.
It is relatively easy to detect which direction is perpendicular
to these sheets in a graphite crystal.
Graphite can thus
be used to monochromate X rays (i.e. isolate one particular
wavelength). Palladium's
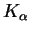 line has a wavelength of
58.9pm.
At what angle would you need to turn the graphitic
sheets of a crystal with respect to an incident X-ray beam
to isolate the
palladium
line has a wavelength of
58.9pm.
At what angle would you need to turn the graphitic
sheets of a crystal with respect to an incident X-ray beam
to isolate the
palladium 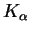 line?
[5 marks]
line?
[5 marks]
Note: the most intense reflection corresponds to the lowest
order of diffraction so monochromation of this reflection
would be most effective.
- 5.
- (a)
- Since photons are particles (albeit massless),
they must obey the uncertainty
principle. Use this fact to derive a relationship between the
uncertainty in a
photon's position and energy.
[5 marks]
- (b)
- Suppose that you manage to measure a photon's position to
an accuracy of 1nm. What is the minimum uncertainty in
the frequency? [4 marks]
- 6.
- The first ionization energy of helium is 24.587eV.
Although the Bohr formula cannot be applied to compute this
value, one could define an effective nuclear charge
by pretending that the Bohr formula does apply.
Compute an effective nuclear charge on this basis.
Give a physical interpretation to the value calculated.
[6 marks]
- 7.
- The Pfund series of the emission spectrum of hydrogen corresponds to
transitions ending at n=5. Predict the wavelengths of the
first four (lowest energy) lines of the Pfund series. [10 marks]
- 8.
- (a)
- What is the minimum speed of a protein molecule of molar mass
28000g/mol in a narrow capillary of length 1.5mm?
Treat the molecule as a quantum mechanical
particle in a one-dimensional box.
[6 marks]
- (b)
- The average molar kinetic energy of molecules held at
temperature T is
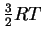 .
If the above system is held roughly at room temperature
(293K),
are quantum mechanical effects likely to be important?
[5 marks]
.
If the above system is held roughly at room temperature
(293K),
are quantum mechanical effects likely to be important?
[5 marks]
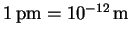
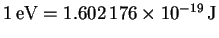
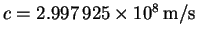
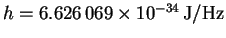
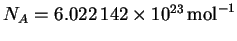
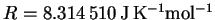
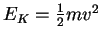 p=mv
p=mv
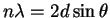
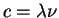
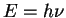
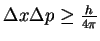
E2 = c2p2 + m02c4
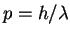
For a particle in a box of length L,
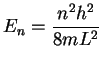 .
.
For a hydrogenic atom,
En = -Z2RH/n2with
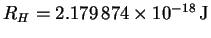 .
.



Up: Back to the Chemistry 2720 test index
Marc Roussel
2000-11-16
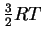 .
If the above system is held roughly at room temperature
(293K),
are quantum mechanical effects likely to be important?
[5 marks]
.
If the above system is held roughly at room temperature
(293K),
are quantum mechanical effects likely to be important?
[5 marks]
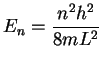 .
.