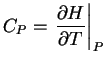
dS = dqrev/T
G = H - TS
![]()
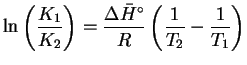
For liquids and solids, a=X. For solutes,
![]() ,
where
,
where
![]() in the usual definition of the
standard state. For gases,
in the usual definition of the
standard state. For gases,
![]() ,
where
,
where
![]() .
.
E2 = c2p2 + m02c4
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
p = mv
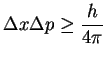
![]()
For a hydrogenic atom,
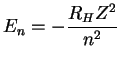 .
.
Vibrational absorption selection rule:
![]() ;
dipole moment
must change during vibration.
;
dipole moment
must change during vibration.
Rotational energy:
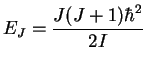
For a diatomic molecule,
![]() and
and
![]() .
.
Rotational Raman transition selection rules:
![]() ;
molecule must be anisotropic.
;
molecule must be anisotropic.
![]()
![]()
![]()
To convert degrees Celsius to Kelvin, add 273.15.
![]()
![]()
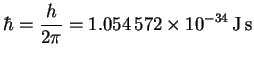
![]()
![]()
Electron mass:
![]()
Specific heat capacity of water:
![]()
Density of water:
| T ( |
|
| 4 | 1.0000 |
| 25 | 0.9971 |