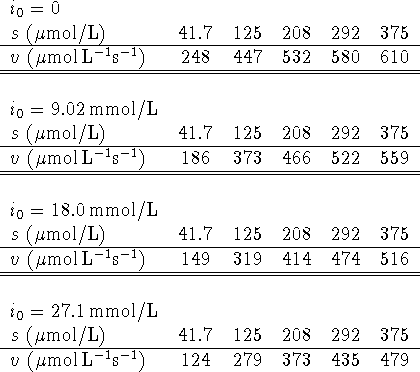
Calculate ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
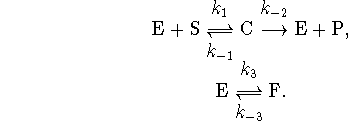
The last reaction is a reversible conformational change leading to an inactive form of the enzyme. Is this mechanism kinetically distinguishable from the Michaelis-Menten mechanism?
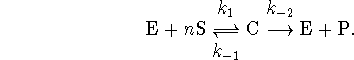
The first step is an instance of cooperative binding: The binding of n molecules of S really happens one molecule at a time, but the first molecule to bind greatly increases the probability that the next will bind so that, on normal measurement time scales, it appears that all n molecules bind simultaneously.
Write your rate law in a form similar to the Michaelis-Menten equation. Describe a graphical method for extracting the constants which appear in your rate equation.