
Up: Back to the Chemistry 2000 assignment
index
Chemistry 2000 Practice Problems on Electrochemistry
Some of these problems may require data from the textbook or other
sources for their solution.
- Dissolved carbon dioxide reacts with calcium metal in a basic aqueous
environment to produce oxalate ions and
calcium ions. Balance the reaction.
- Consider the electrochemical cell
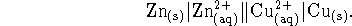
The zinc and copper solutions are both produced by dissolving the
appropriate sulfates. The concentration of zinc sulfate in
the left half-cell is 0.005mol/L and the concentration of
copper sulfate in the right half-cell is 0.002mol/L.
Calculate the voltage
produced by this cell at 298K.
- The highest voltages which can be produced electrochemically are
in the range of 5-6V. Consider the following cell:
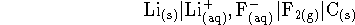
The lithium fluoride concentration is 0.5mol/L and
fluorine is bubbled past the inert electrode at a
pressure of 1atm. Calculate the
voltage produced by this cell at 298K.
- An acidified solution of
sodium iodate (
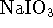 ) with an iodate concentration
of 0.04mol/L and a pH of 4 is prepared. This solution is
used to operate an electrochemical cell, the other half-cell
being the standard hydrogen electrode. The two half-cells share
a common solution; the separation of reactants is achieved by
simply bubbling the hydrogen gas at a pressure of 1atm
over one electrode and not the
other. A brown colour appears at the iodate electrode,
indicating the formation of molecular iodine.
) with an iodate concentration
of 0.04mol/L and a pH of 4 is prepared. This solution is
used to operate an electrochemical cell, the other half-cell
being the standard hydrogen electrode. The two half-cells share
a common solution; the separation of reactants is achieved by
simply bubbling the hydrogen gas at a pressure of 1atm
over one electrode and not the
other. A brown colour appears at the iodate electrode,
indicating the formation of molecular iodine.
- Balance the reaction.
- After a few seconds, a spectroscopic measurement of the
iodine concentration is made. It is found that the
iodine concentration is
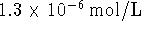 .
If the cell generates a voltage of 1.090V at that time
and the operating temperature is 298K,
what is the
standard reduction potential corresponding to the iodate
half-reaction?
.
If the cell generates a voltage of 1.090V at that time
and the operating temperature is 298K,
what is the
standard reduction potential corresponding to the iodate
half-reaction?
Marc Roussel
Sun Dec 1 12:17:01 MST 1996
![]()
![]()
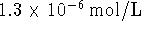 .
If the cell generates a voltage of 1.090V at that time
and the operating temperature is 298K,
what is the
standard reduction potential corresponding to the iodate
half-reaction?
.
If the cell generates a voltage of 1.090V at that time
and the operating temperature is 298K,
what is the
standard reduction potential corresponding to the iodate
half-reaction?