FORMULA SHEET
Constants and definitions: ![]() ;
; ![]() ; 1 ampere (A) = 1 C/s; 1 volt (V) = 1 J/C; 1 farad (F) = 1
C/V; 1 ohm
; 1 ampere (A) = 1 C/s; 1 volt (V) = 1 J/C; 1 farad (F) = 1
C/V; 1 ohm ![]() = 1 V/A; 1 tesla (T) = 1 N/(A m); 1 weber (Wb) = 1 T m2 = 1 J/A; and 1 henry
(H) = Wb/A = 1 J/A2.
= 1 V/A; 1 tesla (T) = 1 N/(A m); 1 weber (Wb) = 1 T m2 = 1 J/A; and 1 henry
(H) = Wb/A = 1 J/A2.
Flux: ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Charge: ![]() .
.
Current: ![]() .
.
![]()
emf: ![]() .
.
Force:
Coulomb’s: ![]() .
.
Lorentz: ![]()
Force on a current (I) carrying wire: ![]() .
.
![]() .
.
Gauss’ law: ![]() .
.
Gauss’ law for magnetism: ![]()
Faraday’s law: ![]()
Ampere - Maxwell law: ![]()
Ohm’s law: ![]() or
or
![]() .
. ![]() for
a metal.
for
a metal.
Conservation of energy law (Kirchhoff’s loop
rule): ![]() around a closed loop.
around a closed loop.
Conservation
of charge law (Kirchhoff’s junction rule): Charge cannot be created or destroyed.
The current flowing into a junction equals the current flowing out.
Electric
Field:
Electric potential: ![]() .
.
Group of point charges: 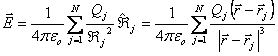 .
.
Continuous charge: 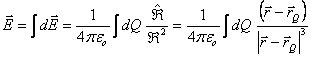 .
.
Electric
Potential:
Potential energy of a charge Q: ![]() .
.
Electric field: 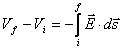 .
.
Constant Electric field: ![]()
Group of point charges: 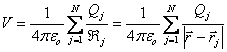 .
.
Continuous charge: ![]() .
.
Magnetic Field:
Biot-Savart law: 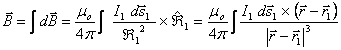 .
.
Circular motion: ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() .
.
Hall coefficient: ![]()
Work: Work-Energy theorem: ![]() .
.
Conservative force: ![]() .
.
Potential energy of a capacitor: ![]() .
.
Potential energy of an inductor: ![]() .
.
Energy density: ![]() .
.
Power: ![]()
Torque: ![]() .
.
Conductor in electrostatic equilibrium: 1. The electric field is zero everywhere. 2.
Excess charge resides on the surface. 3. The electric field is perpendicular to
the surface.
Capacitance: ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
n capacitors in parallel: ![]() .
.
n capacitors in series: ![]() .
.
RC Circuit:
capacitive time: ![]()
charging a capacitor: ![]() .
.
discharging a capacitor: ![]() .
.
Resistance: ![]() .
.
n resistors in series: ![]() .
.
n resistors in parallel: ![]() .
.
power: ![]() .
.
Inductance:
![]() and
and ![]() .
.
self-inductance: ![]() .
.
mutual inductance: ![]() .
. ![]() .
.
n inductors in parallel: ![]()
n inductors in series: ![]()
RL Circuit:
inductive time ![]()
increasing current through the inductor: ![]()
decreasing current through the inductor: ![]() .
.
AC
circuits: ![]() and
and ![]() .
.