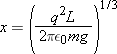ASSIGNMENT #2
DUE ON SEPTEMBER 22, 2005
HAND-IN
CHAPTER #21:
QUESTIONS:
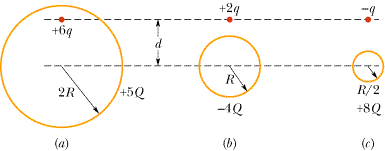
1 Figure 21-12
shows three situations involving a charged particle and a uniformly charged spherical
shell. The charges are given, and the radii of the shells are indicated. Rank
the situations according to the magnitude of the force on the particle due to
the presence of the shell, greatest first.
PROBLEMS:
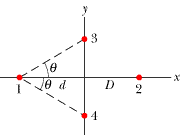
•••18 Figure 21-28
shows an arrangement of four charged particles, with angle q = 30.0° and distance d = 2.00 cm.
Particle 2 has charge q2 = +8.00 × 10–19
C; particles 3 and 4 have charges q3 = q4 =
–1.60 × 10–19 C. (a) What is distance D between the origin
and particle 2 if the net electrostatic force on particle 1 due to the other
particles is zero? (b) If particles 3 and 4 were moved closer to the x
axis but maintained their symmetry about that axis, would the required value of
D be greater than, less than, or the same as in part (a)?
•31 Identify X in the following nuclear reactions: (a) 1H + 9Be → X + n; (b) 12C + 1H → X; (c) 15N + 1H → 4He + X. Appendix F will help.
37
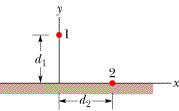
In
Figure 21-37,
particle 1 of charge +4e is above a floor by distance d1
= 2.00 mm and particle 2 of charge +6e is on the floor, at distance d2
= 6.00 mm horizontally from particle 1. What is the x component of the electrostatic
force on particle 2 due to particle 1?
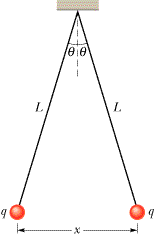
66 In Figure 21-43,
two tiny conducting balls of identical mass m and identical charge
q hang from nonconducting threads of length L.
Assume that q is so small that tan q can be replaced by its approximate equal,
sin q. (a) Show that
|
|
gives the equilibrium separation x of the balls. (b) If L = 120 cm, m = 10 g, and x = 5.0 cm, what is |q|?
ONLINE
CHAPTER #21:
QUESTIONS:
PROBLEMS:
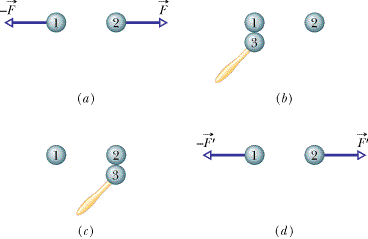
•4 Identical isolated conducting spheres 1 and 2 have equal charges
and are separated by a distance that is large compared with their diameters
(Figure 21-21a).
The electrostatic
force acting on sphere 2 due to sphere 1 is ![]() .
Suppose now that a third identical sphere 3, having an insulating handle and
initially neutral, is touched first to sphere 1 (Figure 21-21b),
then to sphere 2 (Figure 21-21c),
and finally removed (Figure 21-21d).
The electrostatic force that now acts on sphere 2 has magnitude f
.
Suppose now that a third identical sphere 3, having an insulating handle and
initially neutral, is touched first to sphere 1 (Figure 21-21b),
then to sphere 2 (Figure 21-21c),
and finally removed (Figure 21-21d).
The electrostatic force that now acts on sphere 2 has magnitude f ![]() .
What is the ratio f
.
What is the ratio f ![]() /F?
/F?
••25 Earth's atmosphere is constantly bombarded by cosmic ray
protons that originate somewhere in space. If the protons all passed
through the atmosphere, each square meter of Earth's surface would intercept
protons at the average rate of 1500 protons per second. What would be the
electric current intercepted by the total surface area of the planet?
Return
to PHYSICS 2000
HOME